Neural networks are a set of algorithms, modeled loosely after the human brain, that are designed to recognize patterns. They interpret sensory data through a kind of machine perception, labeling or clustering raw input.
source image : link
On the previous articles we study about Linear and Kernel method as
Linear classifier : \(f({\bf x }) = sign( {\bf w }^T {\bf x } + b)\)
Kernel classifier : \(f({\bf x }) = sign( \sum_{i=1}^n \alpha_i k({\bf x }_i, {\bf x }) + b )\)
The adventages for linear classifier is fast for big data (n large). The Kernel classifier work well even for non-linear separable data. Both method are working well on many applications.
However the big problem on the classical Machine learning is that we need to already have a good feature representation. For example, images, text, and speech, a good representation is difficult to obtain by handcrafted feature engineering.
So to handle and learn from the feature representation, we can use a Neural Network
Neural Network
Idea
Before 2012, the default approach to handle the image classification is devided into two approach. First, design some hand-crafted features. Second, train an SVM on these features.
After 2012, the standard method of training this problem is using a deep convolutional neural network. This CNN learns the features and the classifier together in one go. It’s mean that the classifier, which is not an human expert, guides the design of the features.
Let say we are given images \({\bf x }_1,...,{\bf x }_n\). We want to learn a map \(\phi\) that assigns any images \({\bf x }\) with a vector representation \(\phi({\bf x })\)
How can we learn a good feature representation \(\phi\)?
Let the learning machine figure it out. we recall the logistic regression
\[\underset{b \in ℝ, {\bf w } \in ℝ^d }{min} \ \ \ \frac{1}{2} \| {\bf w } \|^2 + C \sum_{i=1}^{n} ln \left( 1 + exp \left( - y_i ( {\bf w }^T \color{red}{ \phi( {\bf x }_i ) } + b ) \right) \right)\]We want to find the feature map and optimize also the \(\phi\). The problem is to search space of all mapping \(\phi\) is too large which restrictions to make.
Natural Neural Network
The idea is our brain also performs classification, for which it learns good feature representations.
On our brain the nodes are called neurons and the edges are called synapses
Artificial Neural Netwoek
A classical neuron model denote by u the neuron’s potential and by v the emitted spike (activation), then
\[v = \sigma(u)\]where the \(\sigma\) is the sigmoid function
\[\sigma(u) = \frac{1}{1+e^{-u}}\]The sigmoid function transforms the real signal into the scale between 0 and 1.
Instead of the sigmoid function, today’s ANN usually use the ReLU (Rectified Linear Unit)activation function which denote below
\[\sigma(u) = max(0,u)\]Neuron to neuron
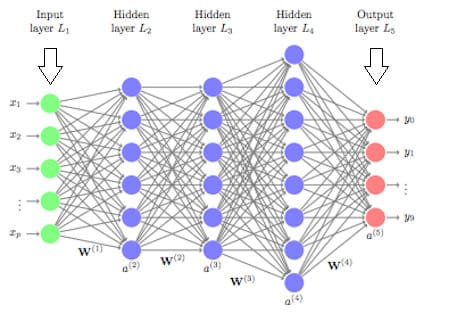
Feed forward ANN Perceptron
\[{\bf v } = \sigma(W^T {\bf v })\]where the v is the vector of activations of all neurons in the network and W = Wij are the weights of the connections of the neurons
\[{\bf v }_l = \sigma(W_l^T {\bf v }_{l-1})\]Similarity with linear classifier
The neural network has the similarity to the linear classifier, the different is just the feature map.
Linear classifier : \(f({\bf x }) = sign( {\bf w }^T {\bf x } + b)\)
Kernel classifier : \(f({\bf x }) = sign( {\bf w }^T \phi({\bf x }) + b)\)
NN classifier : \(f({\bf x }) = sign( {\bf w }^T \phi_W ({\bf x }) + b)\)
The feature map for neural network as below:
\[\phi_W ({\bf x }) = \sigma \left( W_l^T \sigma \left( ... \sigma \left( W_1^T {\bf x } \right) \right) ... \right)\]How to get good weight in this case is we wrap a learning machine around the network and let it figure out good network weights
Conclusion
Artificial Neural Network ANN is motivated by how the brain works. It is consisting of neurons organized in multiple layers with connections. Learning feature representation (network weights) and classifier at the same time.
Convolution Neural Network
For many types of images it makes sense to process only a particular (patches) of images, this is because content could be in any position. Typically one wants to apply filters to the patches to detect “interesting” properties of the images.
Many image filter are based on convolutions.
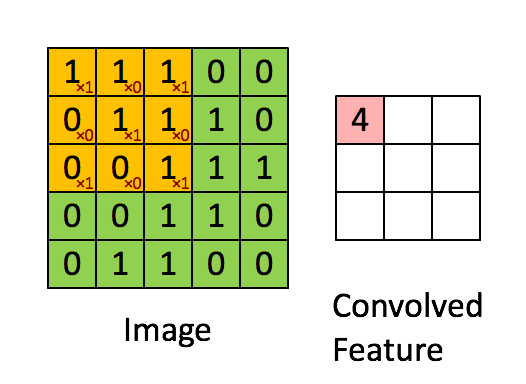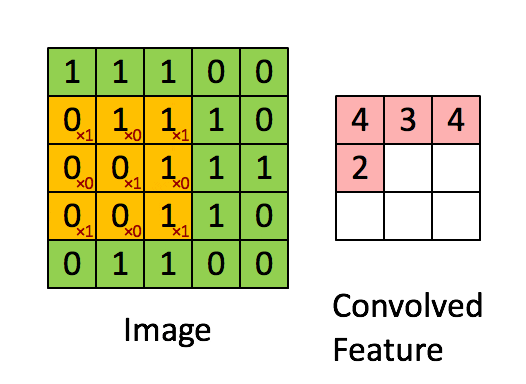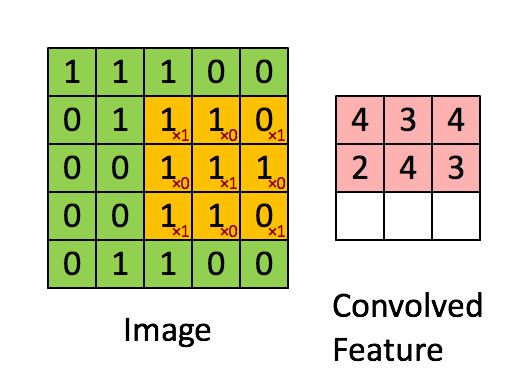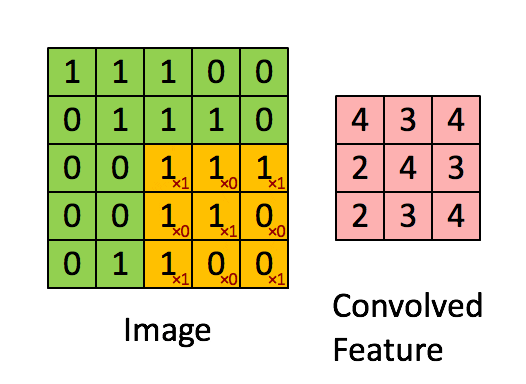
source image : link
The CNN neuron of the same plane are forced to share the same weight Wij weight sharing
Hence, the very same five filters are applied to every patch, no matter where in the image the patch is, invariance against translation of objects in image and drastic reduction in number of parameters.
Conclusion
Convolution Neural Network, instead of handcrafting image features, let the learning machine (logistic regression) figure out good representation. Wrap the learning machine around a CNN and learn a prediction model and an image representation at the same time.

 Convex Optimization Problems on SVM
Convex Optimization Problems on SVM