Machine Learning is reshaping how we live. You may not know it but machine learning is all around you.
The application for example, In the case of Game of Thrones(GoT), we are given the storyline of GoT until now, we want to predict the likelihood of death of characters in GoT. How we can solve this problem?
Predicting the death of characters
- From data to numerical attributes
- Feed attributes into the computer
- Let the computer predict the future
From Data to Numerical Attributes
The idea is we define character attributes that (potentially) might be relevant for prediction of a character’s death, for example, the Age, House Stark, House Targaryen, Married status, How popular in GOT wiki, etc.
Each Character is now a vector of attributes, for example
| House Stark | | 1 |
| Age | | 36 |
| Married | = | 1 |
| Female | | 0 |
| ... | | ... |
Then the color encoding, dead or alive,
Feed attributes into the computer
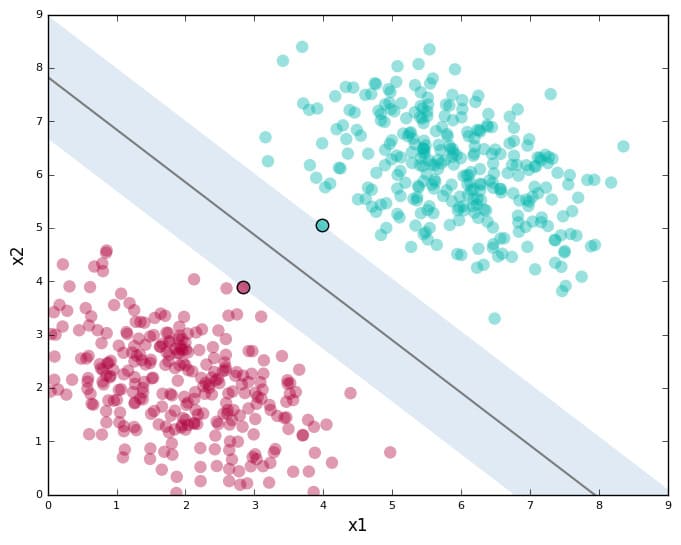
The second step is the computer now computes a smooth separation of the past data. between the death dan alive.
Let the computer predict the future
On the third step, for a character that wants to predict the likeliness of death, we use the separation computed by the computer.
What is Machine Learning?
Learning is the act of acquiring new knowledge, behaviors, skill, values, or preferences and may involve synthesizing different types of information. Or from the other sources, Learning is the ability to learn is possessed by humans, animals, and some machines.
So, what is machine learning, Machine learning is a field of study that gives computers the ability to learn without being explicitly programmed (Arthur Samuel). Computational methods using experience to make accurate predictions (Mhryar Mohri et al). Set of techniques that allow a computer to acquire or improve its ability to perform a task by automatically extracting knowledge from data.
Example of Machine Learning problems
-
Robot Learning Data: Sensor data gained by robots roaming their environments Goal: Robots learning to better navigate
-
Data Mining of electronic health records Data: Electronic health records of patients Goal: Learn to predict which therapies work best for which diseases
-
Speech Recognition Data: annotated recordings of speech (smartphone, customer service hotlines, etc) Goal: Better understand your speech based on experience listening to you
-
Optical Character Recognition Data: human-annotated handwritten digits or letters Goal: better recognize your handwriting
and many more example
Machine learning has a strong impact on all kinds of applications
What can Machine Learning be for you
Core tasks in ML: Theory > Algorithms > Applications
-
Theory, Analyze learning algorithms using techniques from probability and statistical learning theory, in order to understand them better
-
New Algorithms, Design of algorithms that learn faster or more accurately
-
Applications, Get learning algorithms working in applications
Machine learning is interdisciplinary (algorithms, AI, statistics, numerical mathematics, all kinds of application, etc.)
Basic Terminology
Data = Input + Labels, The data consists of inputs and labels.
- Input, the raw data instances x1, …, xn (e.g. source code of computer programs)
- Labels, their annotations y1, …, yn (malware: yes or no)
Training and prediction
Training, use all data (input and labels) to train the computer
Prediction, use the trained computer to predict the (unknown) labels for new inputs.
Formal Problem Setting
Let X and Y be some sets (called input space and label space, respectively)
Training data = \[ { (x_1, y_1), …,(x_n, y_n) } \in \mathbb R^d\]
The x1, …, xn is called inputs and y1, …, yn is called labels.
The goal of machine learning is to write a computer program that learns from the training data a function that accurately predicts on future or unseen data (data test)
the function is called the prediction function, or simply classifier, if Y is a finite set, the elements in Y are then called classes.
The computer program is synonymously also called learning machine or learning algorithm
How can we formally capture whether or not the computer predicts well
Let f be the classifier output after training the computer using the training data. For a new input x with label y the classifier f error when f(x) ≠ y. The error probability P[f(x) ≠ y] measures the quality of the classifier f.
We would like to design computer programs that compute f with error probability P[f(x) ≠ y] as small as possible!
Evaluation and Estimator for Error probability
t-times k-fold cross validation (cv)
function CV(t, k, training_data)
for i = 1:t do
//Randomly split the samples into k sets of the same size (“folds”)
for j = 1:k do
//Use jth fold as test set and union of all remaining folds as training set. Train classifier on training set and predict on test set
end for
end for
return average classification accuracy and standard deviation
//(over the k · t many runs)
end function
Conclusion
- Learning from experience
- Machine Learning = making computers learn from data (usually to make accurate predictions of the future)
- Example: k-nearest neighbor algorithm
- Measure the quality of algorithms using cross-validation
- ML: Strong impact on all kinds of applications
- Many opportunities in this interdisciplinary field (algorithms, theory, applications,…)
- Machine learning plays a key role in technology


 Getting Started with Gulp
Getting Started with Gulp